
Multi-factor authentication is enabled for users at your client, but now you’re being asked the following question:
Is there a way to avoid users working from the office having to enter multiple credentials that are required every time they want to access Microsoft cloud applications?
You can tell them that yes there is a way to solve this situation. The solution is to use Conditional Access policies.
Nowadays users are bombarded with all kinds of requests that try to make them believe that they must reveal their username and password to gain access to content that is not legitimate. These requests have only one goal, that the user falls for the trap and gives the requested information.
Knowing that the user’s account is the gateway to the organization’s data, it stands to reason that enabling multi-factor authentication to reduce the possibility of accounts being compromised is a good decision.
“With strong multi-factor authentication (MFA) in Azure Active Directory (Azure AD), protect your organization against breaches related to lost or stolen credentials.”1
It is possible to create an exception to the multi-factor authentication requirement for users when they authenticate using “Using the location condition in a Conditional Access policy”2 available in Azure Active Directory now call Microsoft Entra ID3.
To meet the customer’s need, the additional Conditional Access policy simply targets the users in question and does not require them to use multi-factor authentication when authenticating from a named location.
A named location can be defined as follows in the following scenarios:
Here are the necessary conditions to be able to achieve the proposed solution:
Access the Microsoft 365 admin center in the client’s tenant.
Then proceed to the Identity admin center.
You are now in the Microsoft Entra admin center.
To access the Conditional access section, go to Protection
Then to Conditional Access
You are now in the Conditional Access management window.
As noted previously, for the proposed solution to be feasible, multi-factor authentication for users must be enabled using a conditional access policy that references named location(s).
This is based on the following scenario which was discussed before:
Let’s start with named locations.
Simply go to the named location management window to be able to create a named location that will be the one from which multi-factor authentication will not be required.
By clicking on Named location, in the Conditional access management window, the location in question can be created.
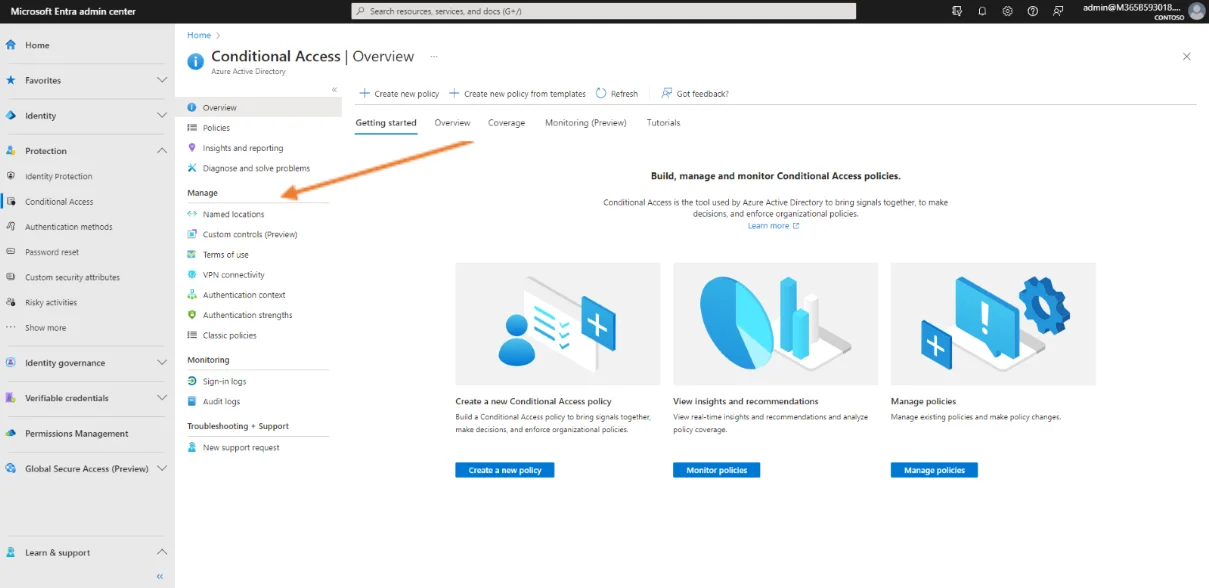
Once in the Named locations management window, click on IP ranges location.
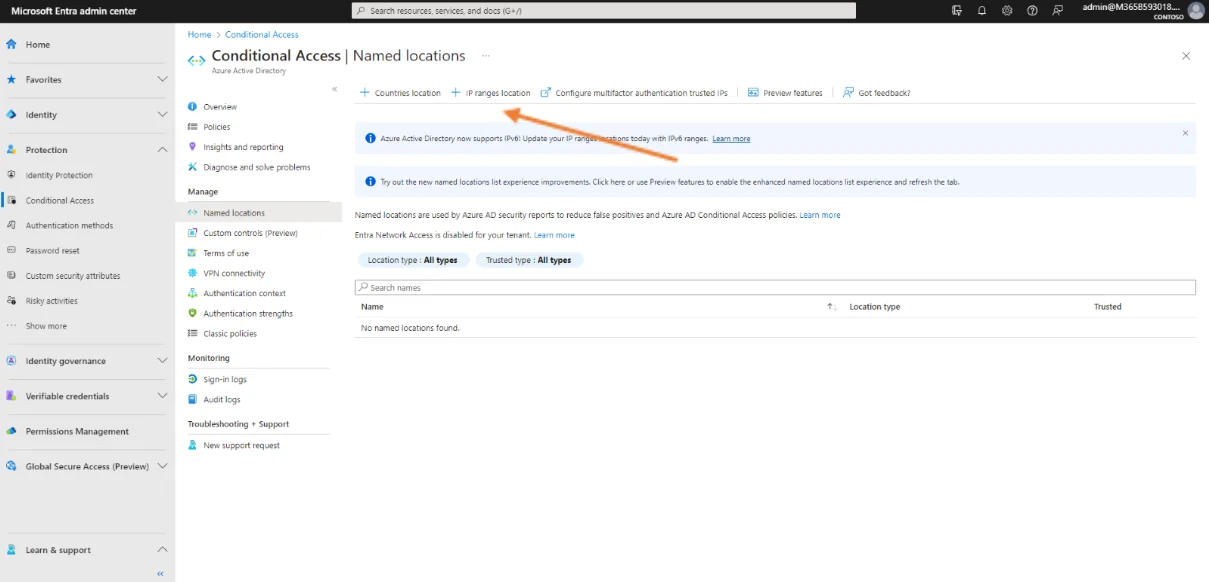
This will open the configuration area.
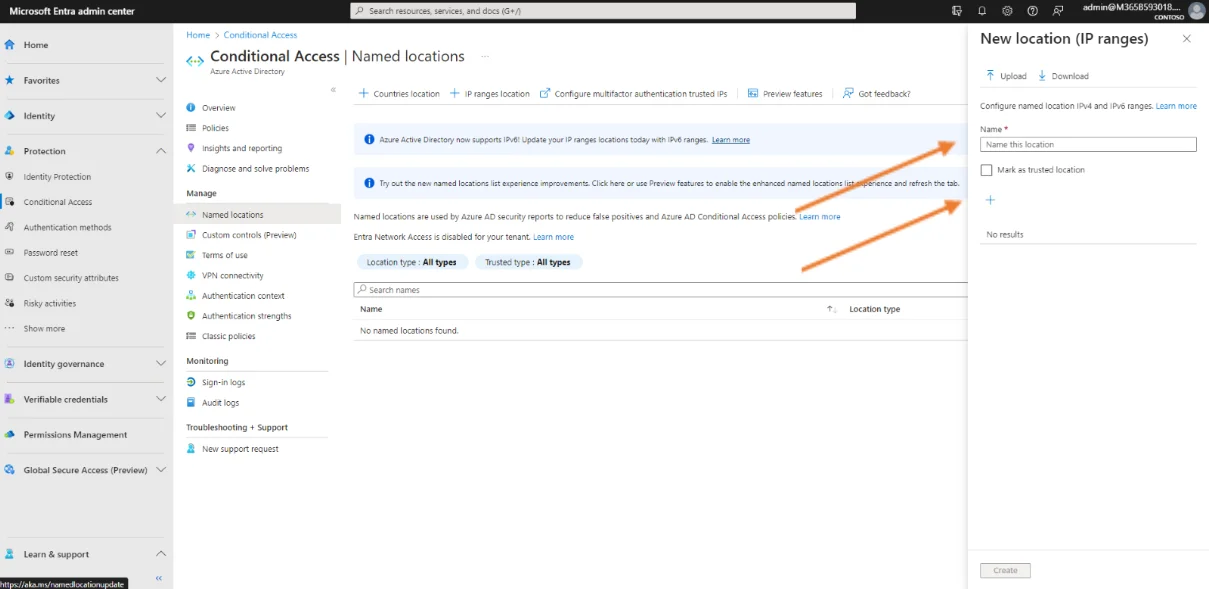
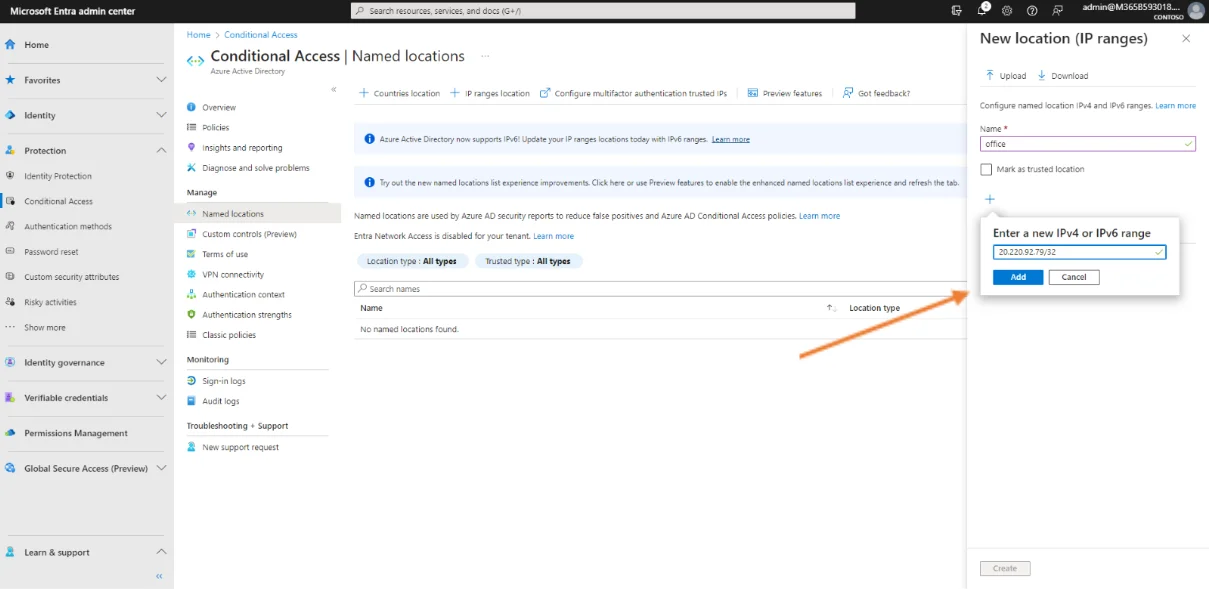
Start by giving the location a name, in our example this name is ‟office”. Then click on the + and enter the public IP address that is used by the customer in his office to access the Internet. This is the one assigned by the Internet provider.
You will be able to find out what this address is without having to contact the Internet provider using the following tool: What Is My IP?
This will give a result for Your IPv4 address: 20.220.92.79 for example. (The address given in this example is from a test environment and does not reflect what can be found at a customer’s site)
Enter this address in the field indicated in the following format 20.220.92.79/32 and then click on Add and finally on Create.
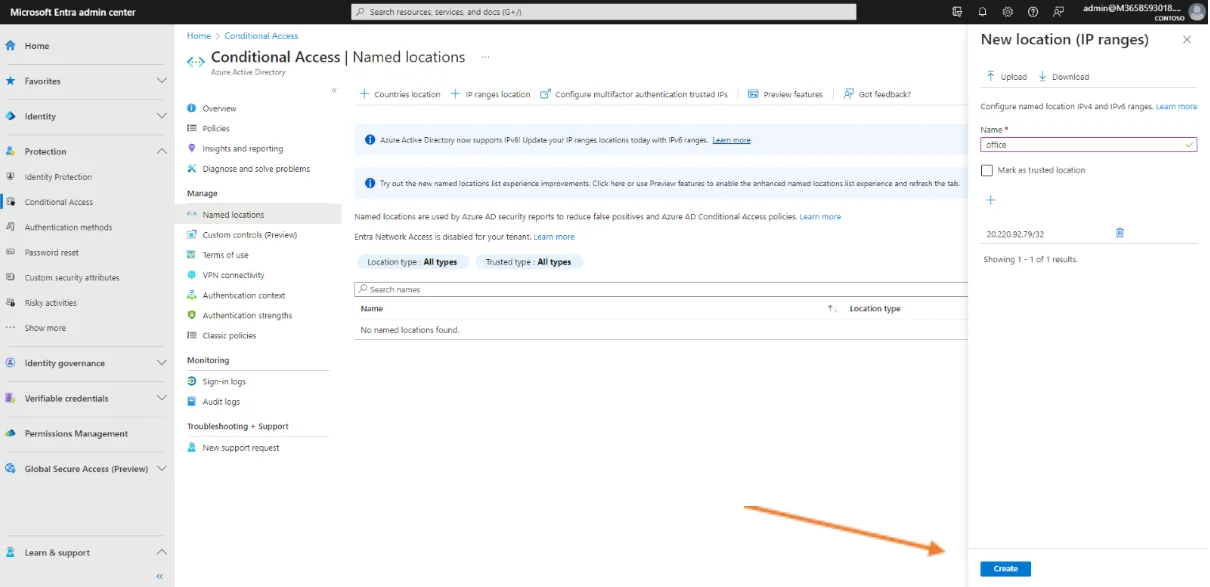
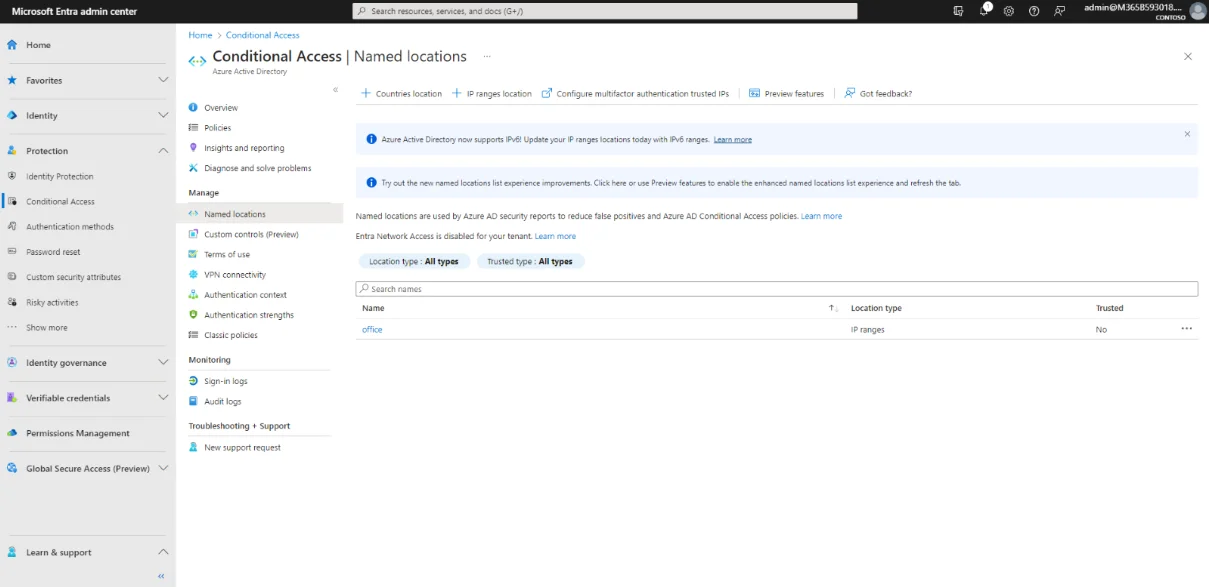
This is the result.
Now create an additional Conditional Access policy ‟no MFA at the office”. This will be applied to users by eliminating the requirement for them to use multi-factor authentication in the office.
Click on Policies
Then click on New policy.
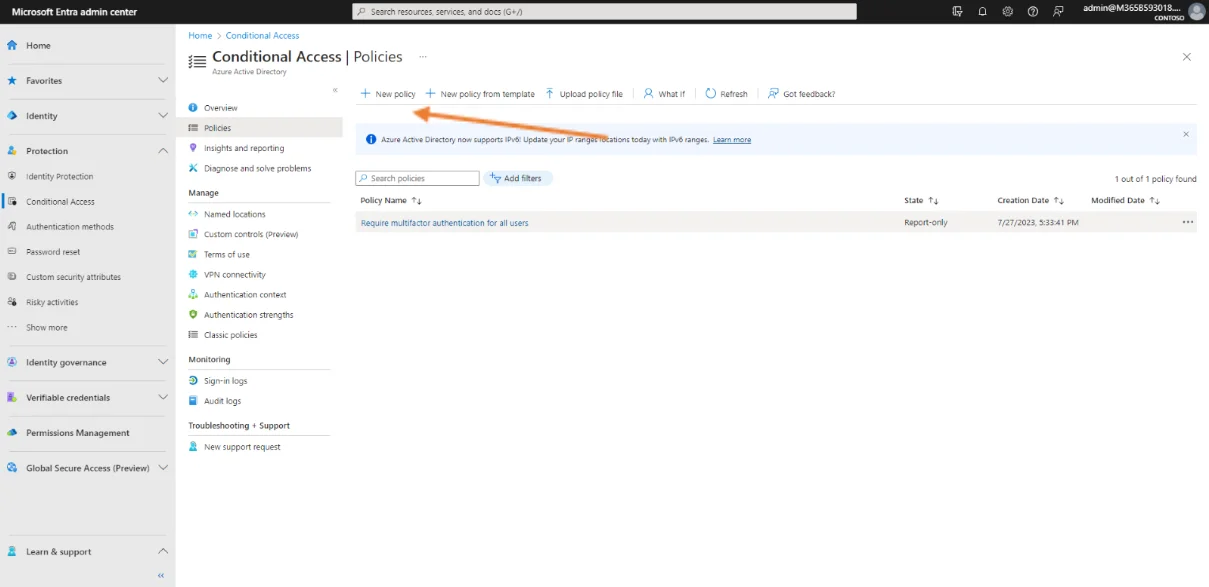
In this conditional access policy management window, the following sections are those of interest to achieve the expected result.
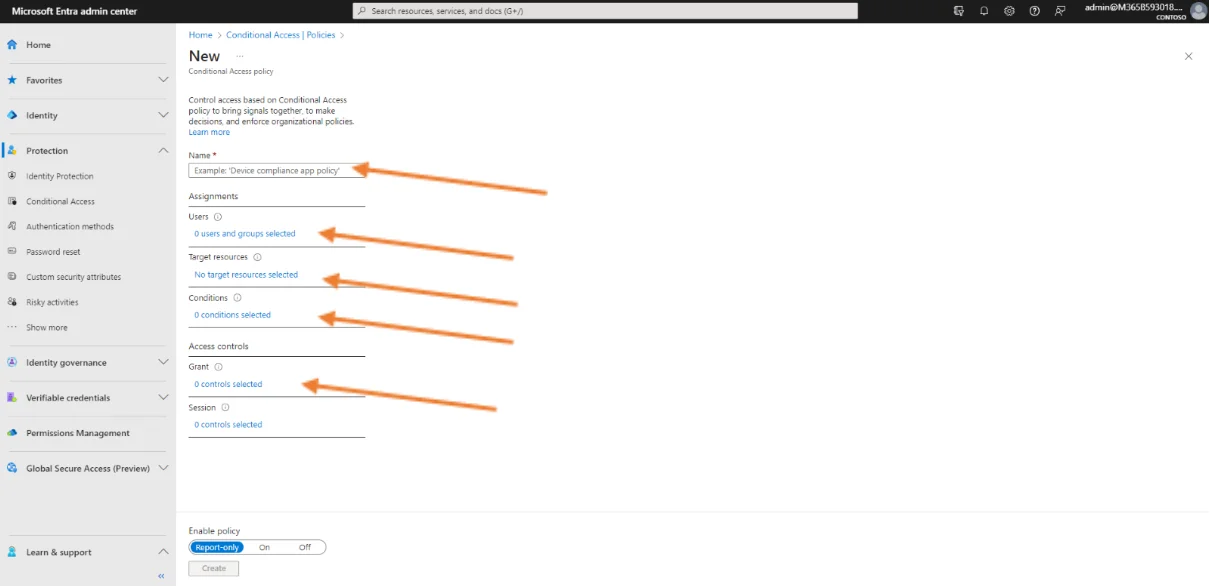
In the example, for the first part of the configuration, add the name “no MFA at the office” as the policy name.
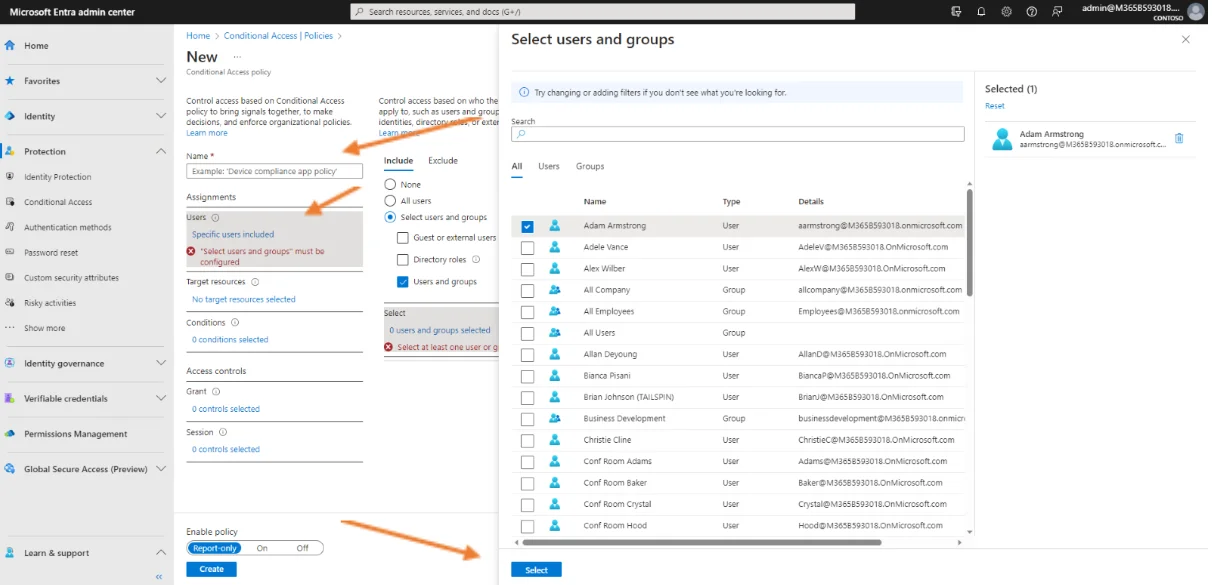
Then, navigate to the Assignments section and in the Users subsection click on Specific users included. In the example a single user was chosen as the one who would be targeted by this policy. Once you have checked the user in question, click on Select. No users are excluded from this policy.
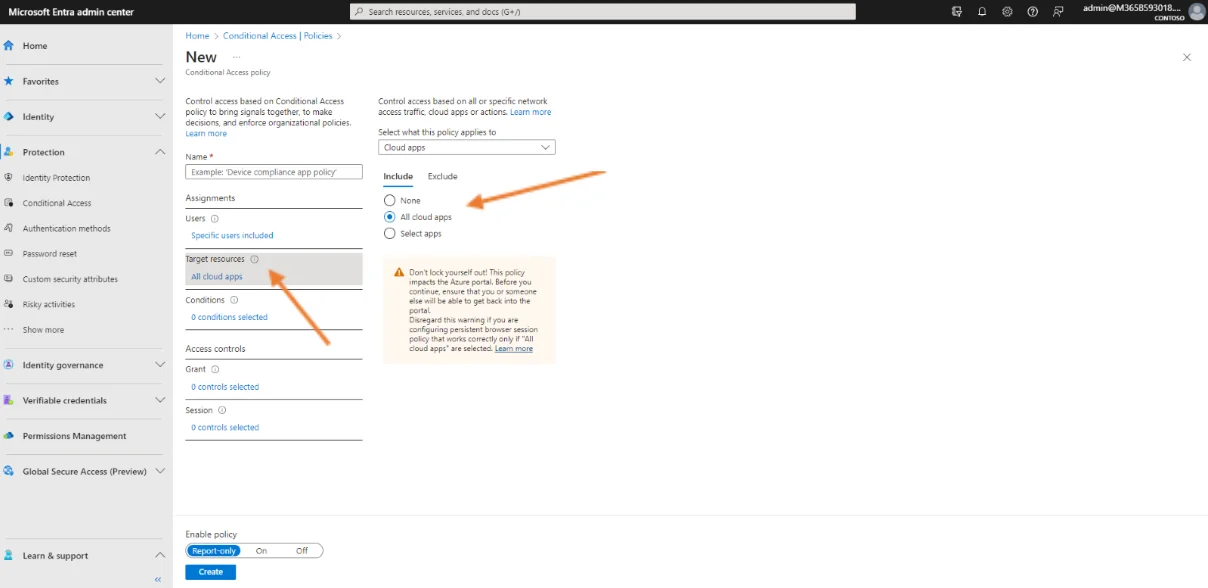
Third, navigate to the Target Resources subsection. Click on “Include All cloud apps”. No applications are excluded from this policy.
Fourth, navigate to the Conditions subsection, click on “0 conditions selected”, then in Locations click on “Any location”, under configure choose Yes and choose “Any locations”.
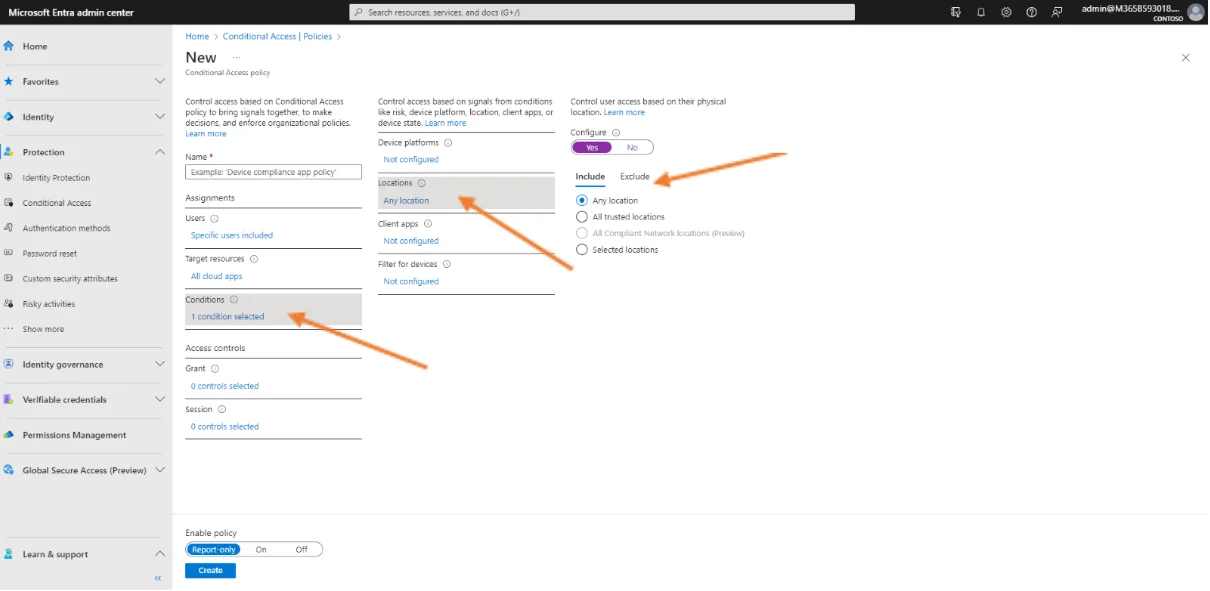
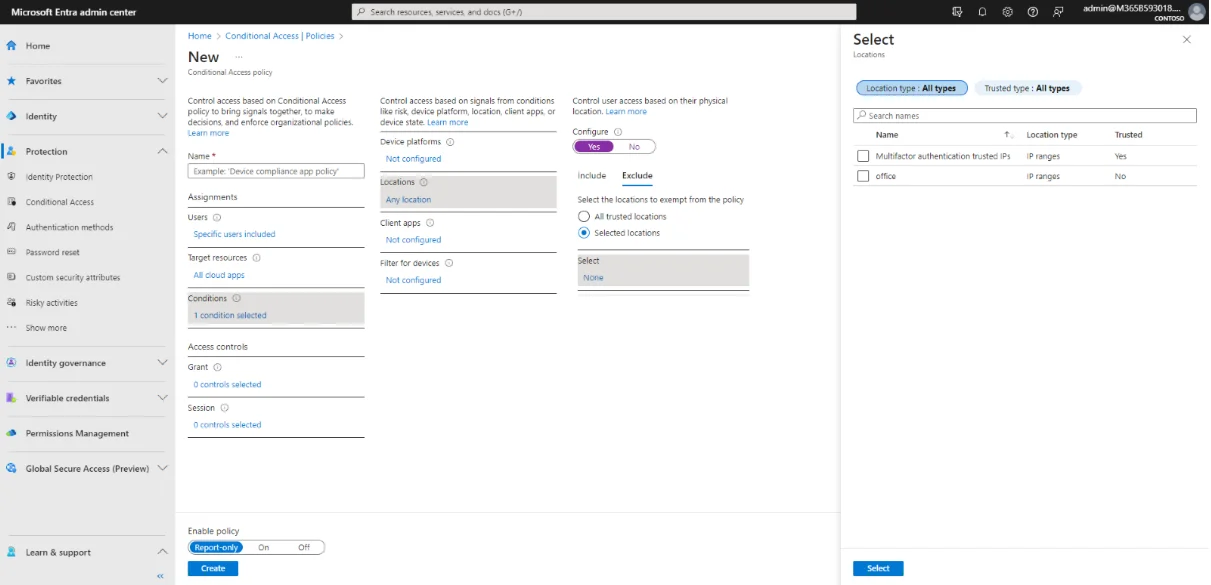
Then, click on Exclude, Selected locations, None and choose the desired location and click Select.
Finally, as far as the configuration requirements, navigate to the Access Controls section in the Grant subsection, click on “0 selected controls”. Then click on Require multi-factor authentication and click Select.
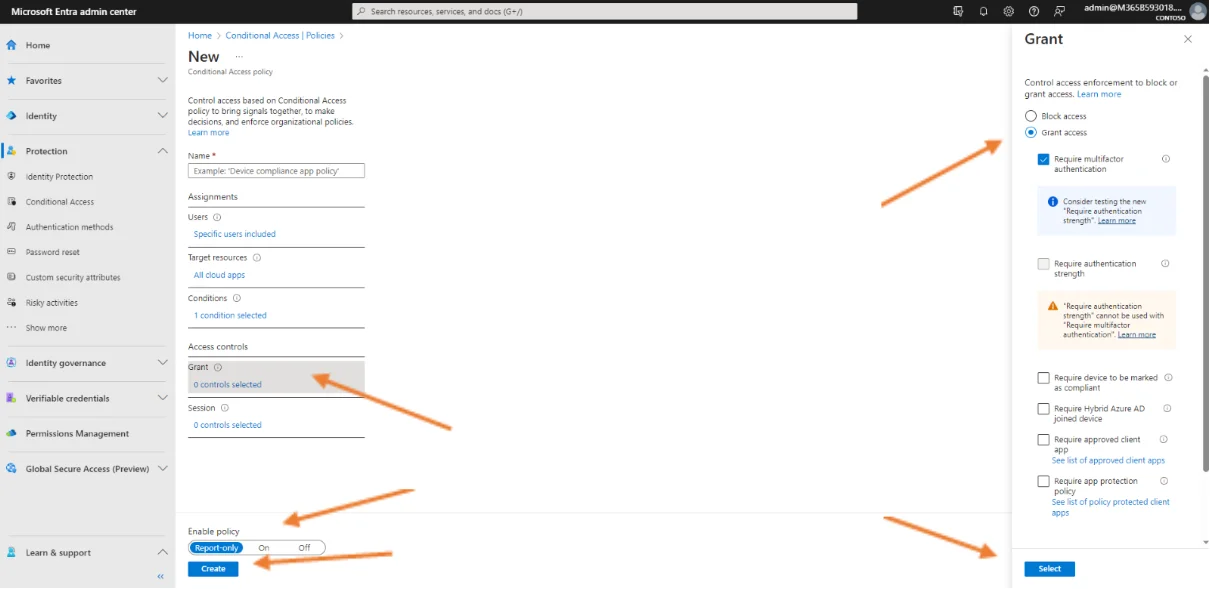
All you have to do is choose On mode under Enable policy then click on Create.
This is the result.
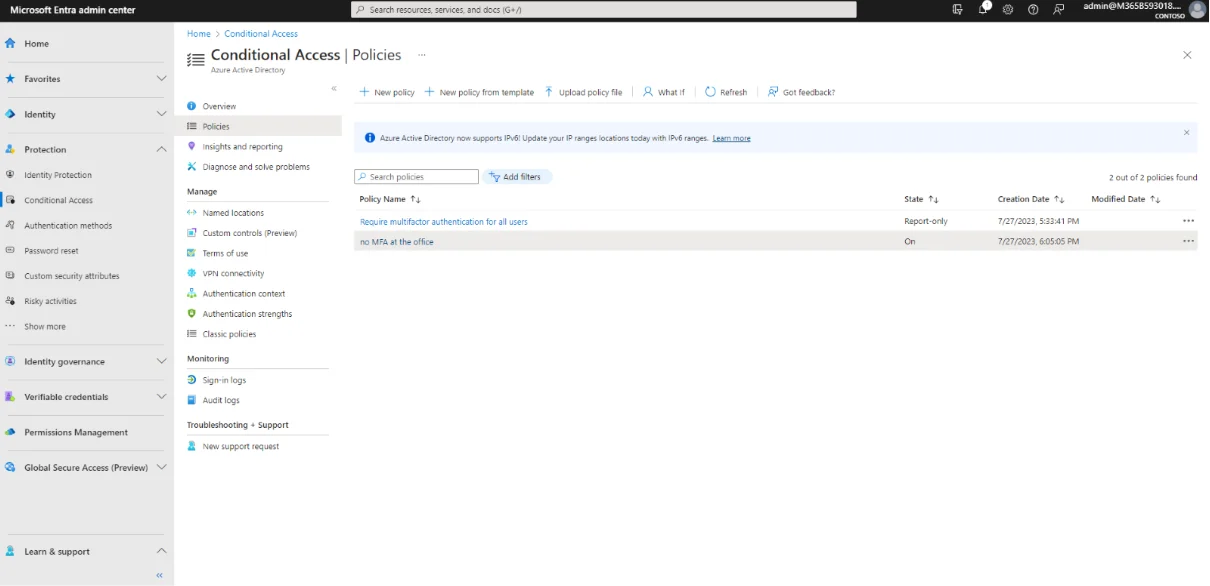
We now need to exclude the user from the “Require multi-factor authentication for all users” policy.
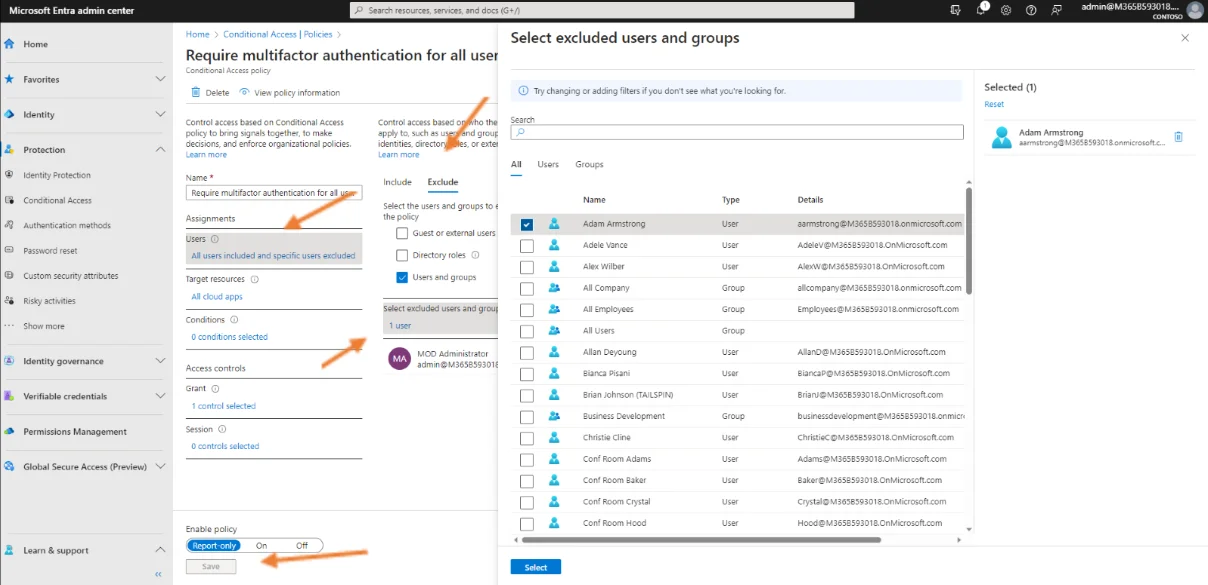
To do this, click on the “Require multi-factor authentication for all users” policy. In the Assignments section, Users subsection, click “All users included and specific users excluded” and on Exclude. Click on “1 user”, because there was already a user excluded from this policy. Put a check mark next to the new user to be excluded, then Select and Save.
As the example has demonstrated, in certain cases, the use of conditional access policies allows you to soften the requirements related to multi-factor authentication.
The example that was used, dealt with the first scenario of those listed:
In fact, the solution provided would lend itself to the second scenario as well:
Either way, regardless of the scenario, the outcome is the same: we can soften the requirements related to multi-factor authentication.
By using conditional access strategies, we can move closer to a work environment that was more common in the past. Not so long ago, users were in the office as well as the infrastructure that was used to meet their needs.
When this kind of environment was the reality, users did not have to authenticate each time they accessed resources that were made available to them.
Now that the infrastructure is in the cloud, he identity that is used to access it has become the main issue.
With conditional access we manage to address the need to ensure that the person accessing the resources is really the person in question and at the same time not to make it inconvenient to access the resources they need.
1 – Multifactor Authentication (MFA) | Microsoft Security
2 – Using networks and countries/regions in Azure Active Directory – Microsoft Entra | Microsoft Learn
3 – Azure Active Directory – Microsoft Entra | Microsoft Security
4 – Providing a default level of security in Azure Active Directory – Microsoft Entra | Microsoft Learn
5 – Enable per-user Multi-Factor Authentication – Microsoft Entra | Microsoft Learn